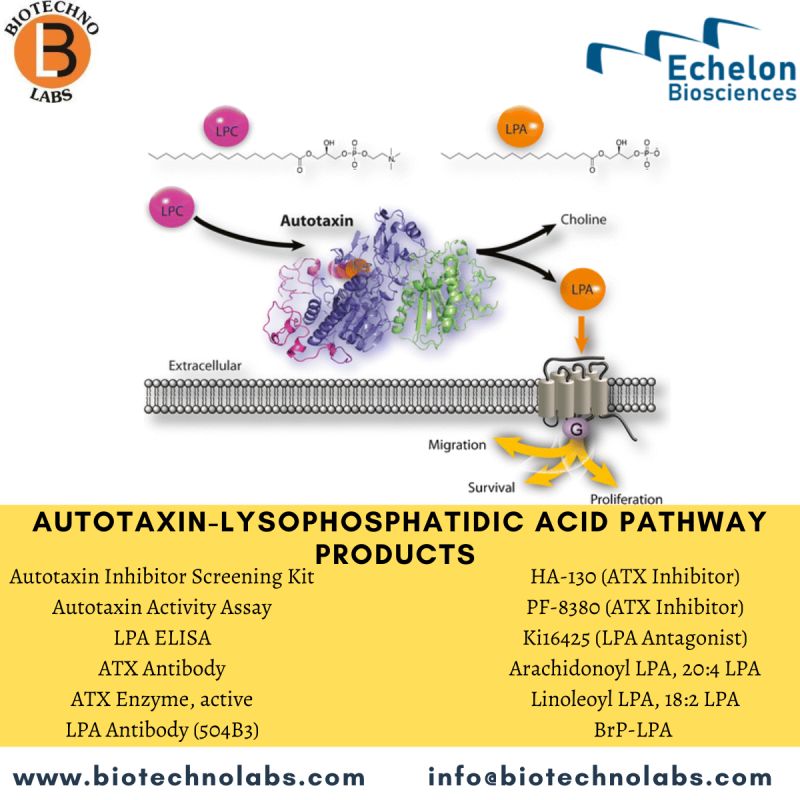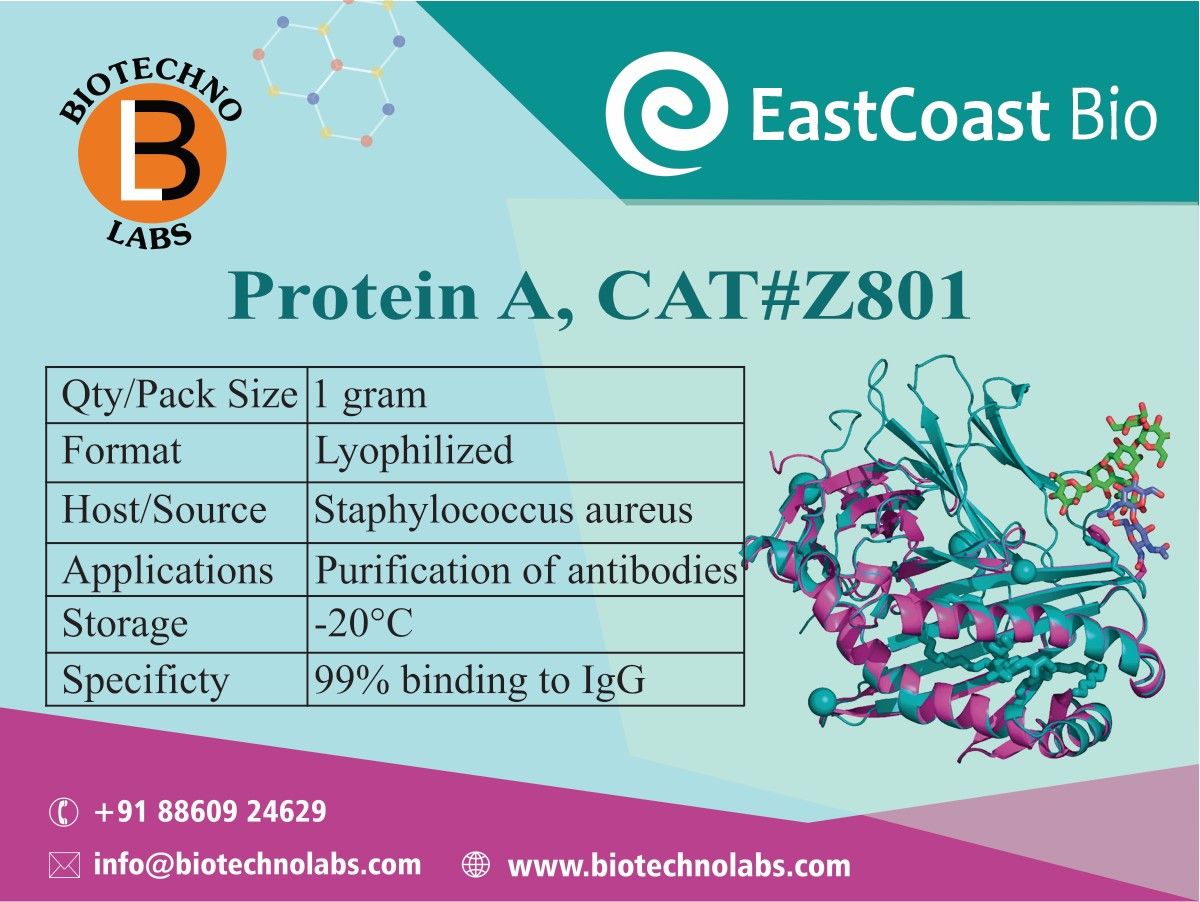
Protein A
Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene, and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. As a pathogen, Staphylococcus aureus utilizes protein A, along with a host of other proteins and surface factors, to aid its survival and virulence. By binding the Fc portion of antibodies, protein A renders them inaccessible to the opsonins, thus impairing phagocytosis of the bacteria via immune cell attack. Protein A is produced and purified in industrial fermentation for use in immunology, biological research, and industrial applications (see below). Natural (or native) protein A can be cultured in Staphylococcus aureus and contains the five homologous antibody binding regions described above and a C-terminal region for cell wall attachment. Chromatographic separation using protein A immobilized on porous substrates is the most widely established method for purifying monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from harvested cell culture supernatants. The choice of protein A as the preferred method is due to its high purity and yield, which are easily and reliably achieved.
BTL Biotechno Labs Pvt. Ltd., a channel partner of East Coast Bio, provides their >99% purified protein A, which has specificity for IgG subclasses of humans, mouse, rabbit, cat, dog, pig, monkey and guinea pig to the Indian scientific community at the best price with the fastest delivery. As a distributor, we prioritise customer satisfaction and strive to maintain strong relationships with our clients. Our commitment to quality, reliability, and affordability sets us apart in the industry. By partnering with East Coast Bio, we ensure that our customers receive the latest advancements in biomedical research, empowering them to make significant strides in their respective fields.
For more details, please follow the link below: