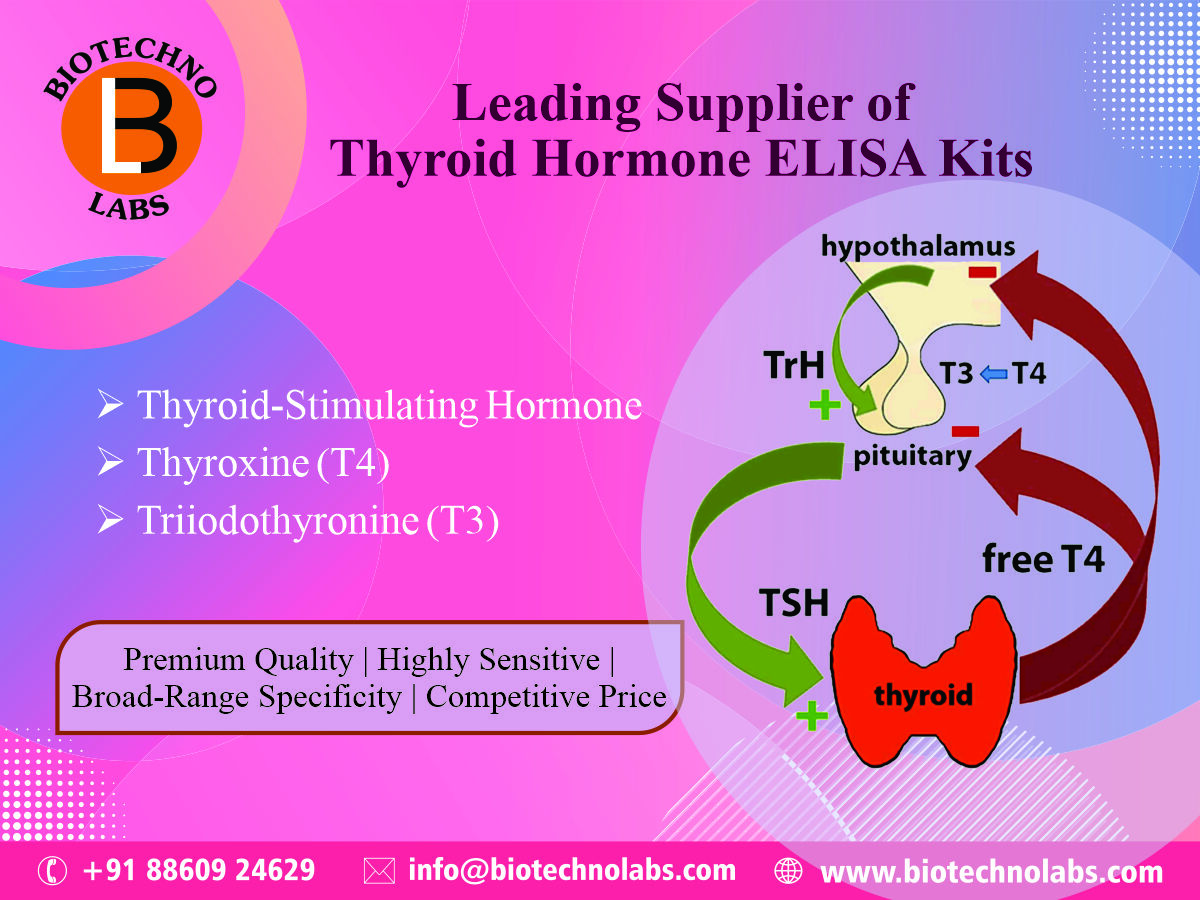
Role of IL6, D Dimer and CRP Level in SARS Cov2
COVID-19 has been infecting people differently. While some people remain asymptomatic, others experience severe consequences. As of now, it is believed that the clinical symptoms of a severe COVID-19 infection include breathing difficulties, chest pain, disorientation, and bluish discoloration of the limbs. Physicians have nevertheless noted a number of cases of respiratory dysfunction and multiple organ failure in COVID-infected individuals. These serious repercussions may manifest in some COVID-19-infected individuals even in the absence of any symptoms.
The inflammatory pathophysiology of severe COVID-19 and other serious disorders involves a cytokine storm, which denotes significant inflammatory activity in response to infection. The majority of the biomarkers examined in COVID-19 patients, including C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)-6, neutrophil count (NC), lymphocyte count (LC), D-dimer, prothrombin time (PT), and transaminases are further non-specific indicators of cellular damage and inflammation. Furthermore, severe COVID-19 frequently results in heart, liver, and kidney failure; as a result, patients with this condition have also had their organ-specific biomarkers examined.
Hence, diagnostic tests such as CPR, D-dimer and Interleukin 6 can help indicate the risk and determine the disease progression.
CRP Level
CRP is a blood test marker for C-reactive protein. It is produced in the liver and measured via a blood test. Higher levels of CRP are detected during infection or inflammation. A value less than 10 mg/L is considered to be a normal level. The CRP test determines the level of inflammation caused by infection in the body. The circulating CRP levels in COVID-19 patients have received surprising attention, and numerous lines of research have demonstrated the predictive usefulness of this biomarker. Studies examining the clinical utility of CRP have found a significant correlation between baseline readings and disease severity.
For instance, studies have demonstrated that CRP correlates with computed tomography (CT) scan severity scores and is superior to NC, LC, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). CRP was identified as a reliable biomarker for directing treatment in a retrospective single-center study involving 145 COVID-19 patients. CRP was defined as an early detector of disease severity. Despite the retrospective, single-center approach, excluding variables with missing values from the analysis strengthens the findings.
CRP levels in 108 COVID-19 patients were examined in order to evaluate CRP's performance as a biomarker of disease severity. In the early stages of the disease, the CRP level and CRP-to-LC ratio exhibited a significant predictive value. Therefore, based on the data, it was concluded that CRP had an "excellent ability" to predict a severe course of COVID-19 in its early stages.
IL-6 Level
With respect to COVID-19, IL-6 has received the most attention among the cytokines, and several investigations have demonstrated a relationship between IL-6 levels and disease severity. Strong correlations were seen between higher baseline IL-6 levels and the need for mechanical ventilation, lung damage shown on CT scans, and other inflammatory markers such as CRP, LDH, ferritin, and D-dimer in patients with severe COVID-19. According to a recent meta-analysis study, IL-6 levels were found to be approximately three times higher in severe COVID-19 patients than in non-severe individuals.
However, multiple outcomes were considered in the studies evaluated in this meta-analysis (ARDS, ICU admission, and death), making it difficult to determine specific IL-6 levels that lead to a given outcome. Regarding the reliability of IL-6 as a treatment response indicator, it was demonstrated that there is no appreciable difference in IL-6 levels between sarilumab responders and non-responders. Thus, the usefulness of IL-6 as a marker of the treatment response is not proven. Studies have demonstrated reduced levels of IL-6 after treatment with antibiotics, antivirals, and glucocorticoids.
COVID-19-infected people suffering from pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, or any cardiovascular disease should get an Interleukin-6 test done.
Ferritin & LDH
LDH is an indicator of cytokine mediated tissue damage and also acts as an inflammatory indicator present in any organ and tissue throughout the body such as including liver, heart etc.
Ferritin is an indicator of inflammation and correlates with the severity of COVID 19.
Coagulation Pathway Biomarkers
In COVID-19 patients, PT and D-dimer levels have been examined to determine whether they can predict a worse prognosis, which is defined as the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), admission to the ICU, and mortality. In a cohort study of 201 patients, it was demonstrated that PT and D-dimer levels were substantially related to the onset of ARDS. Patients with ARDS who passed away had considerably greater coagulation indices than patients who survived. D-dimer and fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products were also considerably higher in moderate disease than in severe disease.
Later, it was discovered that the best cut-off for predicting in-hospital mortality for COVID-19 was a D-dimer level of 2.0 g/mL at admission. D-dimer levels on admission were observed to be higher in ICU patients than in non-ICU patients, and therefore it was concluded that D-dimer may be utilised to triage patients into critical care. The assessment of coagulation indices in the prognosis of COVID-19 patients demonstrated that PT and D-dimer are good markers of a severe disease course.
D Dimer is fibrin degrading protein that is produced when a blood clot dissolves in the body. It remains undetectable until the body is forming and breaking down blood clots. A blood test is performed to detect the D Dimer level in the blood. This test helps in the detection of blood clots in severe COVID-19 conditions. With the severity of the infection, blood clots will start to form in the lungs and throughout the body, which eventually hampers the blood circulation. In response, the body begins to produce more D Dimer for the breakdown of blood clots, which are detectable for about 8 hours before being cleared out by the kidneys.
Coagulation Pathway BiomarkersA COVID-infected patient would require a D-dimer test if they experienced symptoms such as:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Cough with or without blood
- Swelling, pain, redness, and tenderness in the leg
- Elevated heart rate
- Chest pain
- Excessive sweating
- Dizziness
Pregnant women, those who have undergone major surgery (such as hip surgery) or those with pre-existing coagulation disorders may require a D-dimer test if they contract COVID-19 infection.
Emerging Biomarker
miRNAs
miRNAs are non-coding RNAs that bind to the target mRNA sequence and control post-transcriptional gene expression. miRNAs control a wide range of cellular functions, such as differentiation, proliferation, and survival. Host cell miRNAs can interact with viruses during infections and may be involved in the antiviral immune response. In order to better understand the role of miRNAs as possible biomarkers in COVID-19, 34 positive-sense and 45 negative-sense miRNAs that robustly bind to important SARS-CoV-2 genes have been identified. It is proposed that miRNAs might be helpful for tracking the disease at various stages and forecasting the course of the disease.
The D Dimer and IL-6 tests may be useful biomarkers to assess the severity and the clinical outcome of COVID-19. Elevated D-dimer levels typically indicate that a clot has developed in the body and is in the process of breaking down. This clot may lodge in the heart, lungs, or any other important organ, leading to a stroke, cardiac embolism, or pulmonary embolism. Similarly, an increase in IL-6 levels can indicate a cytokine storm, which has been linked to multiple organ failure in COVID-19 patients.
We, BTL Biotechno Labs Pvt. Ltd., provide ELISA kits of all the important biomarkers of COVID-19 (IL-6, D Dimer, CPR, Ferritin and LDH) to the leading Indian scientific community.
For more details, please follow the below link:
https://biotechnolabs.com/products
For product details, please connect with us at info@biotechnolabs.com.